Parameters
Parameters may be used whenever a 3D object requires defined values. The value input can be a numerical constant, single parameter or mathematical expression, optionally containing parameters. Parameters may define object's dimensions or position within a corresponding solid, if used together with geometric constraints. Changing parameter values, all the affected 3D objects are rebuilt. Parameters are not supported in 2D.
Definition of Parameters
Parameters may contain letters and numbers. A parameter must begin with a letter, not with a number. Allowed letters are a... z and A... Z, usage of diacritical marks, Greek or Cyrillic letters or Japanese or Chinese characters is not possible. Definition of mathematical expressions is described in: Mathematic Expressions.
Parameters may be defined in the function PAR (see below), or may be written into the input field instead of numeric values. If a parameter does not exist, you can confirm the creation of a new one. The default numeric value for numeric input is also offered as a default value of the new parameter.
Parameters in File
Once defined, a parameter is stored in a parameter table. The parameter table is a part of 3D space. Parameters are saved and loaded together with the corresponding 3D/2D file (document). If a document contains objects inserted from part files (if a document is an assembly file), then each assembly group has its own parameter table. The parameter table used for an assembly group is, in fact, the parameter table inserted from the corresponding part file.
If a file is inserted into the current file (document), a parameter table of the inserted file is compared with the current parameter table. If new parameters are not defined in the current table, they are accepted. If they exist and have different values, they are rejected and corresponding dimensions are changed to constant values.
Parameters in Scaled Solids
If you scale selected solids and the solids use parametric values, all such values are changed into constants. Similarly, all parametric values are changed into constants if you change units of the current document (millimeters to inches or vice versa). In both cases you are acknowledged before the operation.
Type of Parameters
Parameters are divided into three types:
- Linear parameters. These parameters are used for definition of length, diameter, thickness, fillet radius etc. Linear parameters may be used in mathematical expressions. Value of a parameter corresponds to current units (millimeters or inches).
- Angular parameters. These parameters are used for definition of angles. Angular parameters may be used in mathematical expressions. Value of a parameter is related to angular degrees.
- Thread parameters. This type of parameter can be used for thread definition. For instance, you may use the parameter “t” instead of “M10”. Whenever the parameter “t” is redefined, the correspondent thread is changed. Thread parameters may be used only as single parameters and not in expressions.
Working with Parameters
Add, change or remove parameter values – PAR |
This function allows you to work with all parameters used in the current 3D space and assembly groups. You can:
- Define a new parameter. Select a type of the parameter; define a parameter name and value. Thread parameter values are selected from a list of threads. If assembly groups are present, select a new parameter location – 3D space or an assembly group.
- Change a value. Select a parameter and change its value. You may change values of multiple parameters before the changes are applied to corresponding solids.
- Rename parameters.
- Delete parameters. If a parameter used in geometry is deleted, the corresponding parametric value is changed into constant value.
After changing parameter values, system checks:
- If new values of objects comply. For instance, you cannot define the inner pipe diameter greater than the smaller diameter.
- If the mathematical expression can be evaluated. You cannot divide by zero or value close to zero, you cannot calculate an angle if the sinus is greater than 1 or smaller than -1 etc.
Then, all affected parametric values are recalculated and solids are rebuilt. It is possible that element shapes or positions are incorrect for new parameters and the corresponding Boolean tree cannot be rebuilt. Such solids are highlighted and changes are not finished. You may correct new values and rebuild solids again.
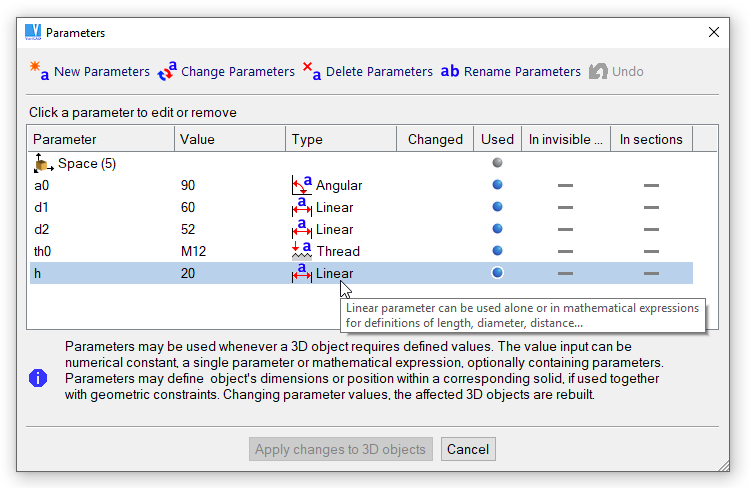
Parameter window. If solid hovers over icons, tool-tip with additional information appears.